Effective nutrition for muscle gain for men
Power to ground is a two-component phenomenon. The diet should “supply” the actively exercising male body with the necessary energy (carbohydrates are its source), as well as provide building material for the “building” of new muscle fibers (protein products).
By and large, the process of gaining mass (in other words, increasing muscle in volume) includes three main steps:
- Muscle stimulation as part of the training process by working with large weights;
- Supply of nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) to the body with food and special supplements (BCAA, protein, vitamin-mineral complexes);
- Quality rest is necessary for muscle recovery and effective growth.
Below we will discuss the key points related to nutrition, the purpose of which is a qualitative increase in body weight (that is, muscle gain).
Basic Rules
Meals for gaining muscle mass for men should be high in calories, so the amount of nutrients obtained from the diet should exceed those consumed during periods of intense training.
Some athletes (especially beginners) are afraid to gain excess fat along with muscles. Of course, there is always the possibility of an additional fat layer appearing at the stage of active mass gain. It is extremely difficult to avoid this. However, you can give the muscles a beautiful relief later with the help of a carbohydrate-free diet (“drying”).
Some athletes go the other way - their weight gain diet is initially "dry" - that is, they both build muscle and get rid of fat. Although this approach has obvious advantages, it overloads the body too much - the body is subjected to daily high-intensity training in a calorie (and, accordingly, energy) deficit. With an improperly organized diet for men, “dry mass gain” can harm the body of athletes.
For example, three meals a day (breakfast, lunch and dinner) are supplemented with two carbohydrate snacks (second breakfast and afternoon tea) and a glass of protein shake before bed.
This approach will help increase the total daily calorie content of the diet and "disperse" the metabolism.
The advantages of such an athlete’s nutrition for weight are obvious:
- There can be much more food than the athlete is used to eating during the day;
- You can increase the number of meals from 6 to 10. This will allow you to evenly distribute the intake of amino acids and other nutrients in the body during the day and speed up your metabolism.
To gain mass qualitatively, an athlete needs to eat every two to three hours - it can be either a full meal or a snack.
So, the first two requirements were considered above, which should be followed during a set of muscle mass:
- Increase in total daily calories;
- Correction of the diet (the number of meals increases from 6 to 10).
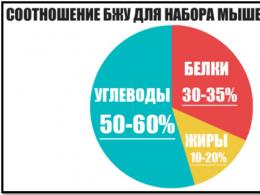
Now it is necessary to pay attention to one more important point - changing the structure of the athlete's diet during training for weight gain, that is, correcting the ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates (hereinafter BJU).
Optimal proportions:
- Proteins - 25-30%;
- Fats - 10-15%;
- Carbohydrates - 50-60%.
This ratio is considered not only "healthy", but also useful for anabolism (raising muscle mass). This structure is designed to provide the body with a sufficient amount of amino acids (“building materials”), as well as give it the necessary energy while “supporting” a minimum amount of vegetable fats.
About Nutrients
Obviously, the basis of nutrition for muscle growth is BJU. Each of these components can also be different. So, proteins are fast (protein, whey protein isolates - are instantly absorbed) and "long" (meat products - are absorbed extremely slowly).
Fast proteins are needed when the athlete's body has been "starving" for a long time and needs to replenish building materials - this happens early in the morning and immediately after an intense workout.
"Long" proteins are required by the body in all other periods of time. The best time to take a protein shake is right before bed.

The best sources of protein for a sports diet for weight gain:
- Meat (preferably poultry);
- Seafood, fresh fish;
- Dairy products: fat-free cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir, milk;
- Eggs;
- Nuts;
- Legumes (lentils, peas, beans).
Along with this, athletes (especially beginners) should avoid the following protein foods:
- Smoked meat;
- Homemade fatty cottage cheese;
- Ham;
- Sausage (particularly salami);
- Sweet milk formulas (eg yogurt).
Carbohydrates are also divided into "fast" and "slow". The first group should include fructose and glucose (compounds that are absorbed at lightning speed and raise insulin levels), the second - dietary fiber, which is slowly absorbed and therefore does not cause a sharp "jump" in blood sugar.
Fast carbohydrates should "get" into the body immediately after training and early in the morning, immediately after waking up. Their task is to “supply” the body with the necessary amount of energy or quickly replenish its massive costs. At all other times, as part of the main meals, athletes need slow carbohydrates (cereals). Before going to bed, any carbohydrates should be discarded.

The best carbohydrates for athletes gaining muscle mass:
- Kashi (millet, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal);
- Pasta (only from durum wheat);
- Black, bran, rye bread;
- Muesli (flakes);
- Vegetables such as potatoes, beets and carrots are recommended to be consumed within reasonable limits - they contain a large amount of starch.
Fats are either saturated (bad) or unsaturated (good). The last group should include vegetable oil, fish, omega 3. Their main task is to reduce the level of "bad" cholesterol in the body. It is better to refuse bad fats (mayonnaise, butter) - their use is fraught with a set of extra pounds.

The best fats:
- Vegetable oils (olive, corn, linseed);
- Avocado;
- Fish.
Power scheme
Consider an approximate menu for building and growing muscle mass:
- Morning - water + simple carbohydrates;
- Throughout the day - slow proteins + complex carbohydrates;
- A few hours before training - light proteins + medium carbohydrates;
- Half an hour before training - free-form amino acids + whey protein isolate;
- During the lesson - sweet water with glucose (if the athlete wants to increase muscle mass), BCAA (when the athlete also wants to “dry out”);
- Immediately after training - simple carbohydrates (juice, gainer) + amino acids in a simple form;
- An hour after class, there should be a full meal;
- In the afternoon - complex carbohydrates + complex proteins;
- Before going to bed - no carbohydrates, "long" proteins (cottage cheese, casein protein) are recommended.
Athletes who are gaining muscle mass should completely abandon sweet and flour confectionery. Of course, they are very tasty, but, once in the body, they instantly cause a jump in blood sugar, stimulate appetite, and, in fact, they themselves are a source of a lot of unnecessary calories. In response to this "behavior", the body immediately begins to convert glucose into fat.
Fast carbohydrates and fats in the diet are also better to limit. In no case should there be any smoked meats, sausages, store-bought sauces, ketchups and mayonnaise in the athlete's daily menu.

It is recommended to eat as many fruits, vegetables and greens as possible - fiber has a positive effect on the digestion process and slows down the absorption of carbohydrates - thus, the blood glucose level rises gradually, and mono-, di- and polysaccharides do not turn into hated fat cells.
Pay attention to the diet. Athletes "on the mass" should not eat several times a day in large portions (moreover, heterogeneous food).
Meals should be frequent, fractional, regular. Only in this case, useful substances enter the body gradually and are better absorbed.
Of course, these recommendations are only general in nature. Each athlete (be it a bodybuilder or a weightlifter) must create an individual diet for himself, based on the characteristics of his own body. Its observance requires a lot of self-discipline, but the result is worth it.