How to calculate weight gain for a girl
In order to lose weight and maintain weight at an optimal level or gain muscle mass, you need to eat a balanced diet. And proper nutrition is impossible without calculating the ratio of BZHU - proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
The amount of BJU is influenced not only by age and gender, but also by lifestyle and the amount of physical activity. In order to calculate the optimal amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, you need to use special formulas. For those who want to lose weight, the formula for calculating BJU will be one, for gaining muscle mass there will be another, and BJU calculations are also different for men and women.
First, you need to understand what BZHU is for the average, relatively healthy (without serious pathologies of internal organs) person. How healthy you are eating now can be determined by looking at yourself in the mirror. Are the sides hanging? Are your ribs sticking out? Are the whites yellowish? Is your face covered in acne? Is your hair falling out? Do you often get sick?
Even at first glance, without being a doctor or nutritionist, you can understand whether your menu needs adjustments. Therefore, let's move on to specifics.

Protein is the building material for our cells. In the body, during the digestion of food, it is broken down into amino acids - universal elements necessary for the growth and strengthening of muscle mass. Protein is also a source of keratin and collagen, necessary for the immune response and the production of red blood cells. A lack of protein will lead to weakened immunity, sagging skin, and oxygen starvation of cells. Excess leads to problems with the kidneys, joints, bladder and general intoxication, since purines are released during protein processing, and we told you why they should be in moderation. We get protein mainly from animal products (meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products), nuts and some vegetables. An ordinary person who is not involved in sports needs 1.5 g of protein per 1 kg of weight per day, and a person leading a physically active lifestyle needs 2 g.
Fats are important for the functioning of the brain, joints, cell membranes, hormonal and lymphatic systems. The diet should contain from 0.8 to 1 g per body weight. If you engage in sports or physically demanding work, you can increase the proportion of fats to 1.5 g. But if your weight exceeds the norm, then it is better to reduce the amount of fats in your diet.
And in order not to gain weight, you need to learn to distinguish healthy fats from harmful ones.
Healthy fats are divided into saturated and unsaturated.
- Saturated fats of animal origin - butter, cheese, milk, lard, meat, etc. - they should be no more than 10% of the total fat in the diet.
- Unsaturated are vegetable fats in liquid form. They are divided into polyunsaturated and monounsaturated. In the first group - sunflower, soybean, nut and seed oils (sesame, cedar, walnut), they should be no more than 40% of the total fat. In the second - olive, rapeseed, avocado, peanut, olives, and they should be given preference over other fats: up to 50% of the total fat.
But what fats should not be on the table are:
- trans fats - surrogate oils obtained artificially. What are these products: margarine, mayonnaise, baked goods, chips, cakes, cookies, ice cream, creams, sauces, candies, etc.;
- oils in which food was fried;
- fats formed during the body's absorption of simple carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are what give us energy and help us digest proteins. The minimum proportion of carbohydrates for a person is 2 g per 1 kg of body weight; for athletes, the norm of carbohydrates is 2-3 times higher. Carbohydrates are processed into glucose, which serves as a source of energy.
They are divided into natural (cereals, fruits, vegetables) and artificial (bakery products, pasta, cookies and sweets), simple and complex (according to the rate of breakdown in the body), and also differ in glycemic index: the higher it is, the more likely it is to gaining excess weight. The most beneficial for the body are natural complex carbohydrates with a low or medium glycemic index and high fiber content.
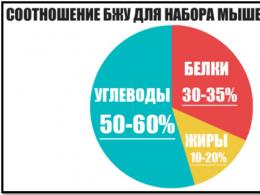
The ratio of BJU for men and women under different conditions
The norm of BZHU per day is 1:1:4.
For weight loss, the BZHU ratio is 4:2:4, that is, with a minimum of fat, an equal amount of proteins and complex carbohydrates.
If the goal is to reduce weight and dry out, then the ratio will look like this - 5:2:3. For girls, BJU values when drying: 4.7:2.3:3
To maintain optimal weight the ratio is: 3:3:4
BJU norm for young women and men engaged in intellectual work: 3.3:2.5:4.2
BJU norm for heavy physical work: 2.7:2.3:5
BZHU for weight gain for both men and women suggests focusing on carbohydrates: 3:2:5
How to determine daily calorie intake
How many calories to consume per day can be calculated using a simple formula for calculating BZH: the desired weight is multiplied by a factor of 24. In this case, the number of kg that you need to lose or gain should be no more than 10. You can divide this process into two stages and calculate the intermediate value, upon reaching which, adjust the caloric intake again.
If you plan to change your weight by more than 10 kg, intermediate stages must be established, firstly, for self-control, secondly, for motivation, and thirdly, so as not to harm your health.
The second way is to use the Mifflin-SanGeor formula. Here you will already need a calculator.
women - K = 10xM + 6.25xP - 4.92xB - 161;
men - K = 10xM + 6.25xP - 4.92x B + 5.
Where M is the desired body weight, P is height, B is age. The obtained result can be corrected by additional coefficients:
1.2 - minimal or no physical activity
1.375 - exercise three times a week
1.4625 - sports 5 times a week
1.550 - intense physical activity 5 times a week
1.6375 - daily fitness classes
1.725 - daily intense physical activity or twice a day
For women: 655 + product of weight and k 9.6 + product of height and k 1.8. The product of age by 4.7 is subtracted from the resulting value.
For men: 66 + (weight x 13.7) + (height x 5) - (age x 6.8).
The average number of calories per day approaches the following values:
All these formulas can be used to calculate BJU both for weight loss and for weight gain and maintaining the norm. In the first two cases, the formula indicates the desired weight, in the third - the actual weight.
Do not forget to make adjustments for climatic conditions, genetic characteristics of your body, temperament, concomitant diseases, and metabolic rate. And diets like 1200 calories a day are only suitable for extreme cases.
How to determine the amount of BJU in products
When buying products in a store, pay attention to the label. Today, the manufacturer is required to indicate the exact composition of the BJU of each product. If you buy products at the market, arm yourself with a ready-made table of nutritional values and calorie content - it is on our website. This way you can always be aware of how many nutrients are in your food. But it is already known that the fewest calories are in fruits and vegetables, and the most are in refined carbohydrates and sweets. Calculating the calorie content of a dish online is possible if the exact weight and calorie content of all components is known.
A person who adheres to proper nutrition does not need to give up his favorite foods. He has the ability to create a menu taking into account BJU so as to get the most out of the products.
It is important to remember that weight loss and weight gain must be gradual, otherwise you can have a nervous breakdown and hormonal imbalance, which will take a long time to treat, with extensive side effects and unpredictable results. And that just a nutrition plan and BJU calculation may not work without exercise, good sleep and a positive mood.
Nutrition for gaining muscle mass: Calories and nutritional supplements
If you want to gain muscle mass, then you cannot do without proper nutrition. The best training program will not produce the desired results of muscle growth if you eat too little and do not consume enough proteins/fat/carbohydrates. The body will simply have nowhere to get the energy to build muscles!
A properly constructed nutrition program for gaining muscle mass should be balanced and contain all the necessary nutrients.

First, a few words for those who initially have a lot of excess fat. You need to lose weight, and only then switch to nutrition to gain muscle mass. Contrary to popular myth, it is physiologically impossible to “pump” fat into muscles. Fat cells do not turn into muscle fibers under the influence of strength training. This doesn't mean you don't need to train. But nutrition should be in a calorie deficit.
Let's look at an example, how many calories/protein/fat/carbohydrates do you need to gain muscle mass?
For a man weighing 75 kg, the following ratio is obtained:
3150 Kcal – 500 calories more than daily value
- 600 Kcal – 150g protein
- 1500 Kcal – 375g carbohydrates
- 1050 Kcal – 115 g fat
In this calculation, protein is 2g/kg of body weight, carbohydrates are 5g/kg, fat is for all remaining calories.
Let's take a closer look at how these numbers are obtained and how to make the calculation for your weight.
Basics of proper nutrition for gaining muscle mass
To grow muscles, you need not only to train properly (at home or in the gym), but also to provide your body with enough energy. No sports supplements (protein, amino acids, creatine, etc.) will give results if you spent all the energy from food during training and there are no calories left for muscle recovery and growth.
How many calories do you need?
Male, weighing 75 kg, with a fast metabolism and low initial body fat.
75*35 = 2625 kcal
2625*1.2 = 3150 kcal
3150 is the number of calories you will need to consume to grow muscle mass. About 500 calories over the norm.
The main building material for muscle growth is protein.
When engaging in strength sports and bodybuilding, you should keep your protein intake at the level 1.5-2.5g per 1kg of body weight. Start with a smaller amount and watch the results; if necessary (slow muscle growth), increase the protein intake.
For example, a man weighing 75 kg needs 112-187 g (460-750 calories - 4 kcal per 1 g) of protein per day.
When gaining muscle mass, choose low-fat sources of protein - chicken breasts, fish, beef, cottage cheese 0-9%, egg whites. In addition to animals, you can also eat plant proteins - beans, lentils, chickpeas. Plant protein is best absorbed when it is consumed with an animal. For example, you can use lentils with vegetables as a side dish for chicken. You can make baked goods from cottage cheese and chickpea flour.
To achieve maximum benefits, many athletes drink protein shakes immediately after training, when the body best absorbs nutrients.

Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body. If there are not enough of them, then weakness, apathy appears, the desire and strength for training becomes noticeably less. When eating to gain muscle mass you will need 4-6g carbohydrates per 1 kg of body weight in a day.
Those. a man weighing 75 kg needs 300-450 g of carbohydrates per day (1200-1800 calories - 4 kcal per 1 g).
All carbohydrates are divided into fast and slow - and this is important when choosing food before and after training. 2 hours before - slow, 1 hour before - fast. Immediately after training, you can consume fast carbohydrates - they will be used to restore spent energy reserves.
An example of slow carbohydrates is side dishes: rice, buckwheat, rolled oats (oatmeal is not “fast”, but traditional!). Fast carbohydrates - fruits, sweets and baked goods. As sources of fast carbohydrates, you should give preference to fruits, because... they contain beneficial vitamins and minerals. But if you have nothing but a bun on hand, and you need to get calories, then you can eat a bun. The main thing is that such cases should be an exception, because Fast carbohydrates contain a lot of calories and are digested quickly, not keeping you full for a long time. Therefore, it is easy for them to consume more calories than they need, which will lead to gaining a lot of excess fat. You need to give up foods containing sugar - sweets, sweet juices and sodas. Pasta can be left in the diet, but watch the calories and do not add mayonnaise and other fatty sauces.
Don't be afraid of slow carbs - if you are gaining muscle mass, you will need a lot of energy for training and recovery. Rice, buckwheat, potatoes, legumes - you don’t need to limit yourself to these foods. The main thing is to monitor your fat intake, i.e. do not fry, but boil/stew dishes. 1 tablespoon of vegetable oil already contains about 100 calories.

All remaining calories after subtracting proteins and carbohydrates are fats. This is about 1-2 g/kg of its own weight.
For example, a man weighing 75 kg needs 75-150 g of fat per day (675-1350 calories - 9 kcal per 1 g).
Don't forget that not all fats should be included in your menu. When gaining muscle mass, it is important to distinguish between harmful (saturated) and healthy (Omega-3, Omega-6) fats.
You will need to give up foods such as butter, pork, fatty sauces and all fast food. Sources of fats in a proper diet should be vegetable oils (in limited quantities), fatty fish, and nuts. When gaining weight, you don’t need to switch to low-fat dairy products - you can eat 9% cottage cheese, 3.2% milk - the main thing is not to go beyond your daily calorie intake.
If you feel better (more alert, have more strength in training) by consuming more carbohydrates, then take 1g/kg of your body weight in fat. If, on the contrary, it is easier for you to train without consuming too many carbohydrates, then increase fats to 2g/kg. No one will tell you “how much to weigh in grams”, since all people are different and to achieve the best result you need to try everything on yourself. Try changing the carbohydrate/fat ratio on training/rest days, perhaps this approach will be more effective for you.
Beginners will find it useful when creating a nutrition plan to gain muscle mass. Nutrition program for gaining muscle mass.
There is no need to cling to numbers and percentages. This is just a starting point. Start with the numbers obtained from the calculation. If there is no progress after a month or two, increase your caloric intake. If you gain too much fat along with muscle mass (gaining a small amount is normal!), then reduce your calorie intake. Try changing the protein/carbohydrate/fat ratios. Some may think that “all this is too complicated, I want a ready-made program!” Start with a meal plan. In the process, you will gain experience and sooner or later you will begin to understand what works for you.
Remember that the only universal recipe for muscle growth is to eat, exercise and sleep more. Anyone who promises to sell you a nutrition plan and gives a 100% guarantee that it will work is simply a scammer. Free cheese is in a mousetrap, and to get a good result you need to work!