How to calculate BJU: features, norms and recommendations
To maintain physical fitness, gain muscle mass or successfully lose weight, a person needs to control his diet, know how to calculate BJU, determine the energy and nutritional value of each meal consumed. Closely monitoring changes in their weight, losing weight people try to get rid of extra pounds as quickly as possible, reviewing their diet and reducing its nutritional value.
But sometimes the desire for a quick result plays a cruel joke with them. Why?
The basic value of the diet
A positive result of losing weight can be obtained by correctly calculating the caloric content of the diet and the energy value of each of the foods consumed. Food refusals, debilitating hunger strikes and dubious mono-diets not only harm the body, but often cause feelings of excruciating discomfort. At the same time, a competent ratio of useful components in the process of nutrition provides the body with the necessary amount of energy for a full life and at the same time helps everyone losing weight to build the figure of their dreams, safely getting rid of extra pounds. Most professional recommendations on how to calculate the BJU for people who maintain their weight, who want to build muscle mass or lose extra pounds, are primarily tied to WHO nutrition guidelines.

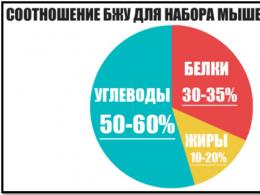
According to professionals, human health and activity depend on the daily intake of proteins (1 g per 1 kg of body weight), fats (1.1 g per the same volume) and carbohydrates (4 g, respectively). This basic ratio of BJU fits well into the "corridor" - from 10 to 15% proteins, from 30 to 35% fats and from 50 to 60% carbohydrates. But many fitness trainers recommend that their wards use the scheme before calculating: 30-35% proteins, 10-15% fats, 50-60% carbohydrates. Or the common ratio: 30/20/50. In this formula, protein has been assigned an uncharacteristic energy function instead of fat.
The history of the emergence of the "golden" weight loss scheme
In order to maintain normal weight, experts have deduced the classic ratio of BJU in grams - 1:1:4. This rate as a percentage looks like this: 14/31/55 and totals 2400 kcal. Nutritionists considered that for effective weight loss of patients, this energy value of the diet can be halved, to 1200 kcal. It is impossible to reduce the daily rate of proteins, so carbohydrates and fats were cut off. From the ratio 4/9/16, which add up to 29, we isolated 14, subtracting 5 units from fat and 9 from carbohydrates. As a result, 4/4/7 remained, which in percentage meant 27/27/46. By reducing fats and rounding proteins with carbohydrates, professionals have developed a universal formula to help you learn how to calculate BJU for weight loss: 30/20/50.

But this scheme is valid only for a diet with a calorie content of 1200 units! Today, daily consumption rates for an adult have been established: proteins - at least 70-105 g (10-15% of the diet per day) and fats with an identical mass in grams, but 30-35% of calories. The difference in the amount of nutrients is due to individual physical activity of a person.
Popular Diet Nutrient Ratio Formulas
In order to calculate the BJU rate based on two common formulas - Harris-Benedict (proposed in 1919 and modified by contemporaries) and Mifflin-San Zheor, developed quite recently (in 2005), you need to decide which one is more suitable for losing weight. For people who ignore sports and prefer passive pastime, the mobility coefficient (KP) corresponds to 1.2; for those who exercise moderately (3 times a week), it rises to 1.375; those who train hard (5 times in 7 days) should take into account CP = 1.4625. All manual workers, who are also passionate about strength exercises, will suit KP 1.6375; engaged intensively several times a day - 1,725; but if physical labor is added to this busy training schedule, then the CP will grow to a value of 1.9. Both schemes for calculating the main daily calorie use this parameter. In the first (Harris-Benedict), the calculation goes like this: 655.1 + 9.563 x weight in kg + 1.85 x height in cm - 4.676 x age. The result is then multiplied by the CP. This calculation has a small error for a modern person (about 5%), so more often nutritionists use the second formula.

Knowing your height and weight, you can also calculate the basic metabolic rate (BOV) according to the Muffin-Jeor scheme (as they also call it, the Mifflin-St. Jeor formula) for women: 9.99 x weight in kg + 6.25 x height in cm - 4.92 x age - 161; for men: 9.99 x weight in kg + 6.25 x height in cm - 4.92 x age + 5 for digestion of food) and multiply the amount by the activity coefficient: SEC \u003d (BOV + BOV x 0.1) x KP.
With the calorie calculated in this way, a person can maintain his weight, but in order to lose weight, you need to create a deficit by reducing it by 500 kcal. For comfortable weight loss, we calculate the calorie corridor. To do this, add 100 kcal (upper limit) to the result obtained and subtract 250 kcal (lower limit) from the original figure. For example, if the diet should be 1500 kcal (2000 - 500), then the lower limit of the corridor will be 1250 kcal, and the upper limit will be 1600 kcal. Taking into account the calorie content of nutrients: proteins (4 kcal), fats (9 kcal) and carbohydrates (3.75 kcal) per 1 gram, respectively, you can calculate the calories of BJU and the amount of each of the nutrients in the diet. Proteins will be 1500 x 0.3: 4 - approximately 113 g, fats - 1500 x 0.2: 9, i.e. approximately 33 g, carbohydrates - 1500 x 0.5: 3.75 (approximately 200 g). Thus, the energy value of proteins in the diet will be 450 kcal (113 g x 4), fat - 300 kcal (33 x 9), and 750 kcal of carbohydrates (200 x 3.75).
Squirrels
Critics of this method of calculating the ratio of nutrients using the daily caloric intake of the diet draw attention to a significant imbalance in nutrition: an excessive amount of protein, a lack of fat and a small amount of carbohydrates.

Before calculating the BJU on the advice of nutritionists who adhere to the method described above, it must be taken into account that an excess of proteins leads to: increased stress on the internal organs (the kidneys and liver are especially affected); an increase in the concentration of urea in the blood; putrefactive dyspepsia (rotten proteins in the colon); excessive load on the gastrointestinal tract. An abundance of protein in the diet is contraindicated in people suffering from diabetes (type 2), which is often the case with obesity.
Fats
Reducing the vital environment for the breakdown of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K leads to a violation of their energy and plastic function. The deterioration of the skin, nails and hair is an external manifestation of a deficiency of fats and vitamins. - this is "night blindness", D - depression, loss of strength, muscle weakness, conception problems, osteoporosis, diabetes and obesity, E - a decrease in its antioxidant effect, the formation of blood clots, the development of atherosclerosis of blood vessels; K - decrease in blood clotting, increased capillary permeability, deterioration of tissue regeneration. Fats are often called the "secret" of female beauty. Fitness trainers often urge, before calculating BJU, to pay attention to WHO standards and not to allow excessive fat reduction. Even for very strict diets, the lower critical bar for the intake of an important nutrient is 0.8 g per 1 kg of weight. It is better to reduce the caloric content of the diet by eating healthy fats (vegetable oils) and reducing the amount of fast carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates
The most valuable components of these substances are disaccharides and monosaccharides. Their balance ensures the full functioning of the muscular system, strengthening it and forcing it to work intensively. With a lack of these substances, losing weight experience general exhaustion, malaise, malfunctions of the central nervous system. In the case of an excess of incoming carbohydrates, a person is threatened with obesity, diabetes mellitus and problems with the digestive organs.

It is known that these components of products give energy to the body and nourish the brain, so the diet should contain a sufficient amount of complex (indigestible) or slow carbohydrates that give saturation and strength. And the consumption of fast simple carbohydrates is best minimized and not eat them in the afternoon, when the body is most predisposed to convert them into fats.
To correctly calculate the ratio of nutrients in the diet, nutritionists and sports nutritionists advise using individual weight in kilograms as the main parameter. In this case, the protein norm will correspond to world standards (1 g per 1 kg of weight), and the required one (400-500 units) will be created due to an adequate reduction in fats and carbohydrates. It is necessary to reduce them proportionally, and in case of violation of the border norms, consider the main WHO recommendations, changing the total calorie content. Only in this case it will be possible to correctly calculate the amount of BJU, without forming a skew in nutrition, and, as a result, weight loss will proceed comfortably and safely for health.

Only for athletes who have been involved in strength training for a long time, people who have been friends with sports all their lives, the process of building muscle by burning subcutaneous fat (drying the body) is associated with an increased intake of lean protein along with a decrease in the amount of carbohydrates in the diet. These events take place in conjunction with a whole program of recommendations, therefore, with moderate physical activity, experts do not advise using them on their own.
BJU: how to correctly calculate their number in one dish
Having dealt with the calorie content of the daily diet and calculated the energy value of each of the nutrients in the diet, it is necessary to determine how much proteins, fats and carbohydrates are contained in each of the prepared dishes. To calculate, you need to arm yourself with an arsenal of tools: a kitchen scale, a calculator, raw food calorie tables - and start a food diary. It is they who will help to calculate the BJU of a dish once, and in the future use ready-made values. In addition, the diary will become a source of information about your eating habits, which, in case of violations, can always be corrected. To begin with, we weigh all the products and calculate their total calorie content, including the energy value of nutrients in raw form. We also find out the mass of the finished dish (be sure to subtract the weight of the pan). Water has no calories. For example, the energy value of 100 grams of dry buckwheat is 336 units, the porridge from it is boiled soft and weighs 200 grams, but the total calorie content remains the same - 336 units. Therefore, 100 grams of finished porridge will have a calorie content of 168 units.

In fried dishes, 20 percent must be added to the nutritional value of the main product - the energy value of the absorbed oil during heat treatment. Grilled chicken becomes a third more caloric, and dried fish, due to moisture loss, doubles. In salt, along with absent. The broth takes one fifth of the total calories of raw foods (20%) that are boiled in it (meat, fish, mushrooms or vegetables). Berries and fruits give the compote a third of their calories (30%).
Fitness trainers in practice recommend, when self-calculating the individual ratio of BJU, not to go beyond the minimum values: protein (at least 1 g per 1 kg of weight), fats (at least 0.8 g per 1 kg) and carbohydrates - at least 50 g per day (in conditions of compliance with a low-carb keto diet with a predominant amount of proteins in the diet). If the starting body weight of a person before losing weight is large enough, then it is better to calculate the BJU in stages (after every 5-10 kilograms lost).